
Return a new group of given shape and type, filled with zeros.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: | Group with the given shape and dtype filled with zeros. |
Examples
>>> dana.zeros((2,2))
Group([[0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0]],
dtype=[('f0', '<f8')])
>>> dana.zeros((2,2), dtype=int)
Group([[0, 0],
[0, 0]],
dtype=[('f0', '<f8')])
See also
Return a new group of given shape and type, filled with ones.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: | Group with the given shape and dtype filled with zeros. |
Examples
>>> dana.ones((2,2))
Group([[1.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 1.0]],
dtype=[('f0', '<f8')])
>>> dana.ones((2,2), dtype=int)
Group([[1, 1],
[1, 1]],
dtype=[('f0', '<f8')])
See also
Return a new group of given shape and type, without initialising entries.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: | Group with the given shape and dtype filled with zeros. |
Notes
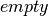 , unlike
, unlike 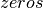 , does not set the group values to zero, and may
therefore be marginally faster. On the other hand, it requires the user
to manually set all the values in the group, and should be used with
caution.
, does not set the group values to zero, and may
therefore be marginally faster. On the other hand, it requires the user
to manually set all the values in the group, and should be used with
caution.
Examples
>>> Group.empty((2,2))
Group([[6.94248367807e-310, 1.34841898023e-316],
[1.34841977073e-316, 0.0]],
dtype=[('f0', '<f8')])
See also
Create a new group of zeros with the same shape and type as another.
| Parameters: | other (array) – The shape and data-type of 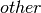 defines the parameters of the
returned group. defines the parameters of the
returned group. |
|---|---|
| Returns: | Group of zeros with same shape and type as 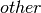 . . |
Examples
>>> x = np.arange(6)
>>> x = x.reshape((2, 3))
>>> x
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]])
>>> np.zeros_like(x)
array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
See also
Returns a group of ones with the same shape and type as a given array.
| Parameters: | other (array) – The shape and data-type of 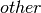 defines the parameters of the
returned group. defines the parameters of the
returned group. |
|---|---|
| Returns: | Group of ones with same shape and type as 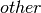 . . |
Examples
>>> x = np.arange(6)
>>> x = x.reshape((2, 3))
>>> x
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]])
>>> zeros_like(x)
group([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
See also
Create a new group with the same shape and type as another.
| Parameters: | other (array) – The shape and data-type of 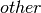 defines the parameters of the
returned group. defines the parameters of the
returned group. |
|---|---|
| Returns: | Uninitialized group with same shape and type as 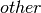 . . |
Examples
>>> x = np.arange(6)
>>> x = x.reshape((2, 3))
>>> x
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]])
>>> np.zeros_like(x)
array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
See also